Model Flavors¶
There are three differnet types of models: average, R(V)+ dependent prediction, and shape fitting.
Average models¶
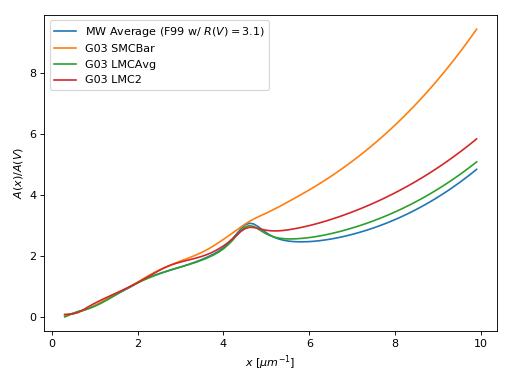
These models provide averages from the literature with the ability to interpolate between the observed data points. For the Milky Way, one of the R(V) dependent models with R(V) = 3.1 (see next section) are often used for the Milky Way ‘average’. Models are provided for the Magellanic Clouds from Gordon et al. (2003). Models for the Milky Way still to be added (both UV/optical/NIR and IR).
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
R(V) (+ other variables) dependent prediction models¶
These models provide predictions of the shape of the dust extinction given input variable(s).
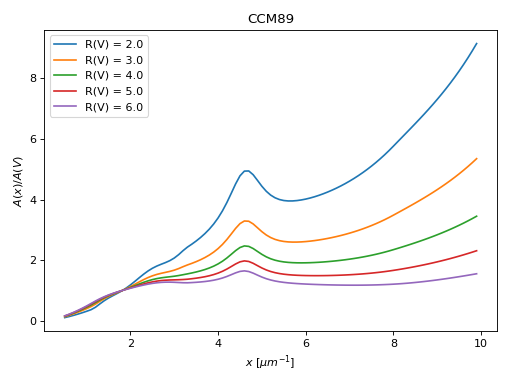
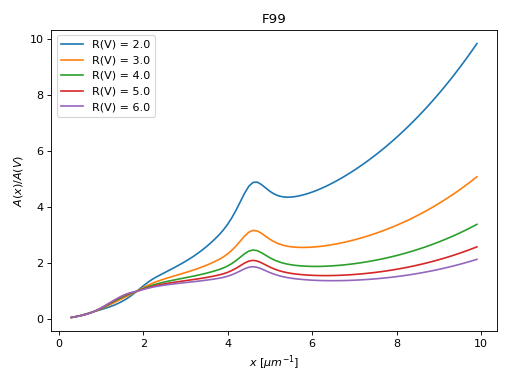
These include CCM89 the original R(V) dependent model from Cardelli, Clayton, and Mathis (1989) and updated versions F99 (Fitzpatrick 1999). These models are based on the average behavior of extinction in the Milky Way.
In addition, the (R(V), f_A) two parameter relationship from Gordon et al. (2016) is included. This model is based on the average behavior of extinction in the Milky Way, Large Magellanic Cloud, and Small Magellanic Cloud.
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
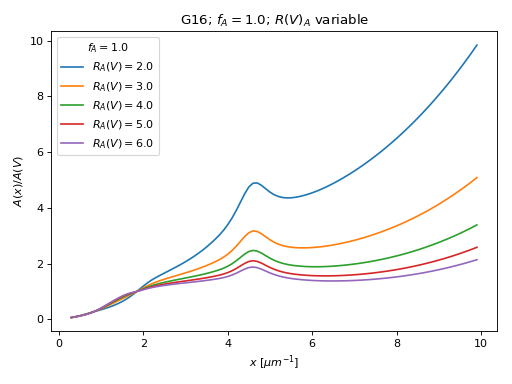
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
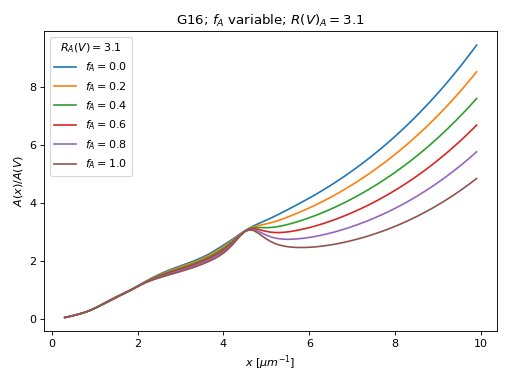
Shape fitting models¶
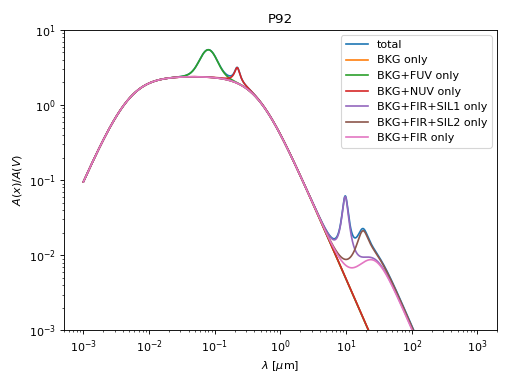
These models are used to fit the detailed shape of dust extinction curves. The FM90 (Fitzpatrick & Mass 1990) model uses 6 parameters to fit the shape of the ultraviolet extinction. The P92 (Pei 1992) uses 19 parameters to fit the shape of the X-ray to far-infrared extinction.
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
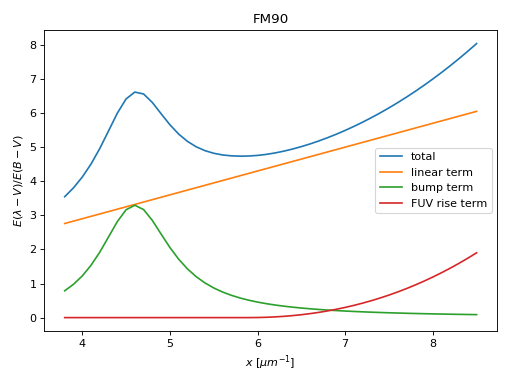
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)